Electrical Engineering ⇒ Topic : Compensation Theorem with d.c
|
|
| Samual
| |
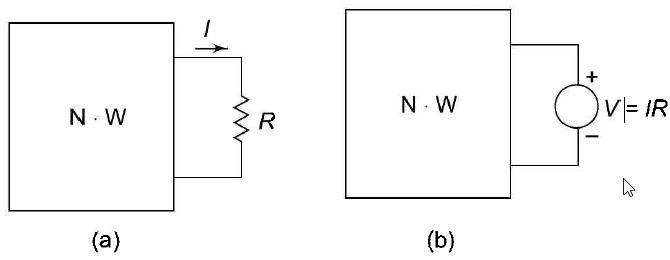
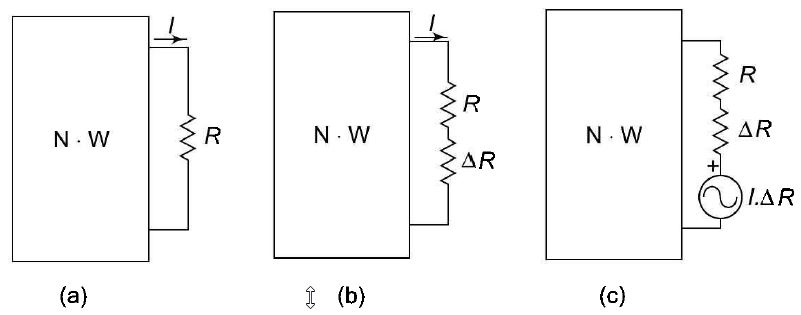
Compensation Theorem The compensation theorem states that any element in the linear, bilateral network, may be replaced by a voltage source of magnitude equal to the current passing through the element multiplied by the value of the element, provided the currents and voltages in other parts of the circuit remain unaltered. Consider the circuit shown in Fig. 1 (a). The element R can be replaced by voltage source V, which is equal to the current /passing through R multiplied by R as shown in Fig. 1(b) figure (1) This theorem is useful in finding the changes in current or voltage when the value of resistance is changed in the circuit. Consider the network containing a resistance R shown in Fig. 2 (a). A small change in resistance R, that is (R + ΔR), as shown in Fig. 2 (b) causes a change in current in all branches. This current increment in other branches is equal to the current produced by the voltage source of voltage I. ΔR which is placed in series with altered resistance as shown in Fig. 2 (c).
figure (2) | |
|
| |
!! OOPS Login [Click here] is required for more results / answer