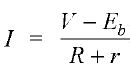Electrical Engineering ⇒ Topic : Battery Charging Circuit
|
|
| Maninder
| |
Battery Charging Circuit Fig. (a) shows the battery charging circuit. A d.c. source of suitable magnitude is connected in series with a rheostat R, ammeter and the battery to be charged. Ensure that polarity is con-ect i. e. positive terminal of d.c. source should be connected to the positive terminal of the battery.The charging current is adjusted to the required value with the help of rheostat. As the charging process proceeds, the terminal voltage of the battery rises but the charging current is kept constant by adjusting the value of rheostat R. The terminal voltage of the battery and specific gravity of electrolyte are checked at regular intervals of time. When the terminal voltage ceases to rise, the specific gravity of electrolyte reaches the value 1.28 and there is enough gassing at the plates, the battery is fully charged. It is then taken out of the charging circuit. The entire charging process may take several hours. Calculations. When the battery is being charged, its e.m.f. acts in opposition to the applied voltage. The applied voltage V sends a charging current I against the back e.m.f. Eb of the battery. The input power is VI but the power being supplied to the battery is EbI. The power EbI is converted into chemical energy which is stored in the battery. FIGURE (A) Charging current, I where R = resistance of rheostat in the circuit r = internal resistance of the battery The charging current is kept constant throughout (by adjusting R) except towards the finish of charge. | |
|
| |
| Maninder
| |
Battery Charging Circuit Fig. (a) shows the battery charging circuit. A d.c. source of suitable magnitude is connected in series with a rheostat R, ammeter and the battery to be charged. Ensure that polarity is con-ect i. e. positive terminal of d.c. source should be connected to the positive terminal of the battery.The charging current is adjusted to the required value with the help of rheostat. As the charging process proceeds, the terminal voltage of the battery rises but the charging current is kept constant by adjusting the value of rheostat R. The terminal voltage of the battery and specific gravity of electrolyte are checked at regular intervals of time. When the terminal voltage ceases to rise, the specific gravity of electrolyte reaches the value 1.28 and there is enough gassing at the plates, the battery is fully charged. It is then taken out of the charging circuit. The entire charging process may take several hours. Calculations. When the battery is being charged, its e.m.f. acts in opposition to the applied voltage. The applied voltage V sends a charging current I against the back e.m.f. Eb of the battery. The input power is VI but the power being supplied to the battery is EbI. The power EbI is converted into chemical energy which is stored in the battery. FIGURE (A) Charging current, I where R = resistance of rheostat in the circuit r = internal resistance of the battery The charging current is kept constant throughout (by adjusting R) except towards the finish of charge. | |
|
| |
!! OOPS Login [Click here] is required for more results / answer