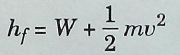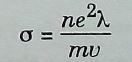Electrical Engineering ⇒ Topic : Thermionic emission
|
|
| Peter
| |
Thermionic emission is the process of electron emission from the surface of the metal into surrounding space by heating the material.Photoelectric equation is given by where hf = total energy content of a single quantum of light incident on a metal surface 'h' is called Planck's constant. W = work function m = mass of an electron ν= velocity of an electron On the basis of free electron model the electrical conductivity (σ) of metal is given by :- λ= mean free path (=ντ ) ν=-mean velocity of electrons N = number of electrons m = mass of an electron At very low temperature, some metals acquire zero electrical resistance and zero magnetic induction ; the property known as superconductivity.The transition from the superconducting state to conducting state is reversible.Important superconducting elements : Aluminium, zinc, cadmium, mercury, lead.Typical superconducting compounds and alloys : Pb2 Au, PbTl2, SnSb, CuS, NbN, NboN,NbB and ZrC. | |
|
| |
!! OOPS Login [Click here] is required for more results / answer